Catalan - Wikilangs Models
Comprehensive Research Report & Full Ablation Study
This repository contains NLP models trained and evaluated by Wikilangs, specifically on Catalan Wikipedia data. We analyze tokenizers, n-gram models, Markov chains, vocabulary statistics, and word embeddings.
📋 Repository Contents
Models & Assets
- Tokenizers (8k, 16k, 32k, 64k)
- N-gram models (2, 3, 4, 5-gram)
- Markov chains (context of 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5)
- Subword N-gram and Markov chains
- Embeddings in various sizes and dimensions (aligned and unaligned)
- Language Vocabulary
- Language Statistics
Analysis and Evaluation
- 1. Tokenizer Evaluation
- 2. N-gram Model Evaluation
- 3. Markov Chain Evaluation
- 4. Vocabulary Analysis
- 5. Word Embeddings Evaluation
- 6. Morphological Analysis (Experimental)
- 7. Summary & Recommendations
- Metrics Glossary
- Visualizations Index
1. Tokenizer Evaluation
Results
| Vocab Size | Compression | Avg Token Len | UNK Rate | Total Tokens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
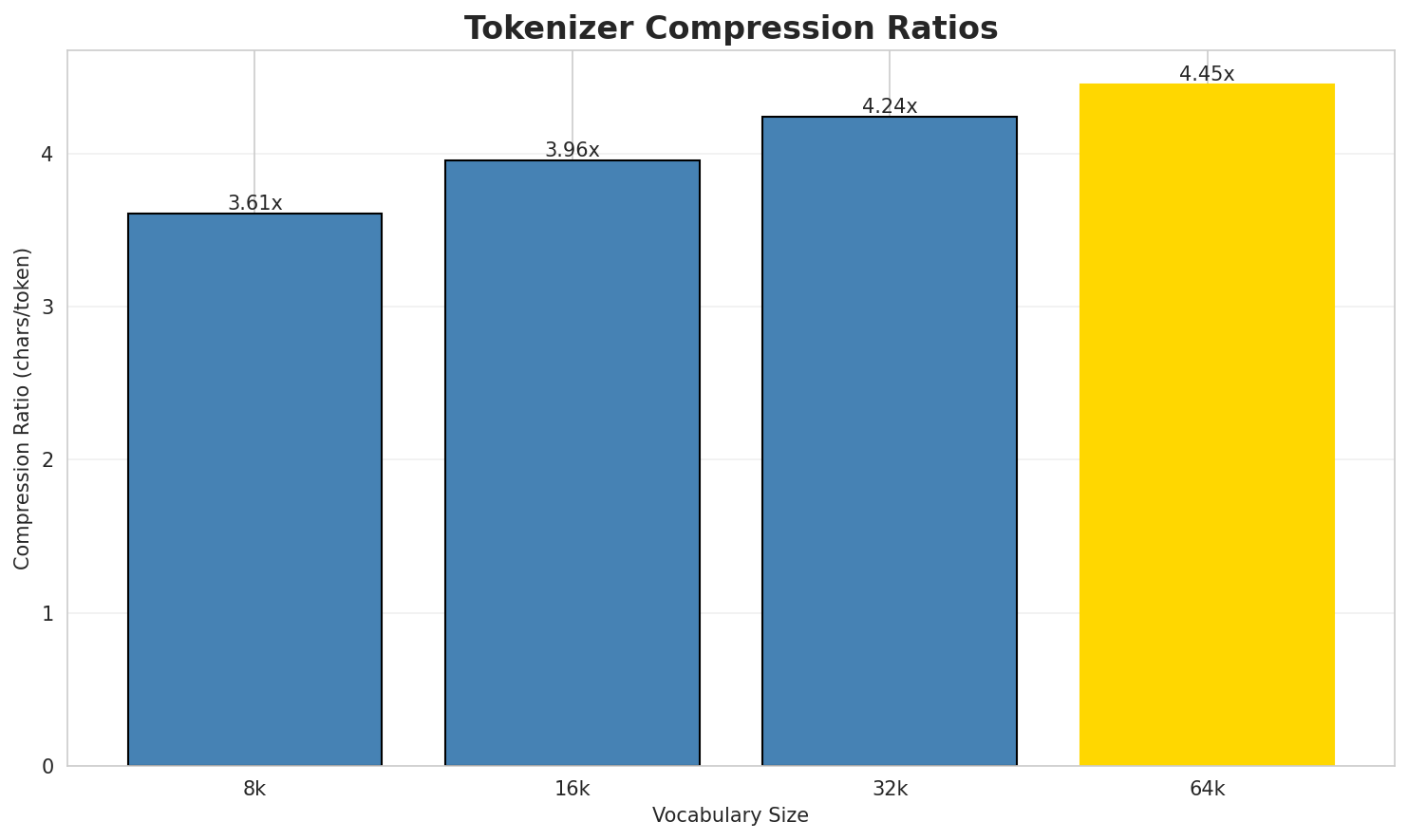
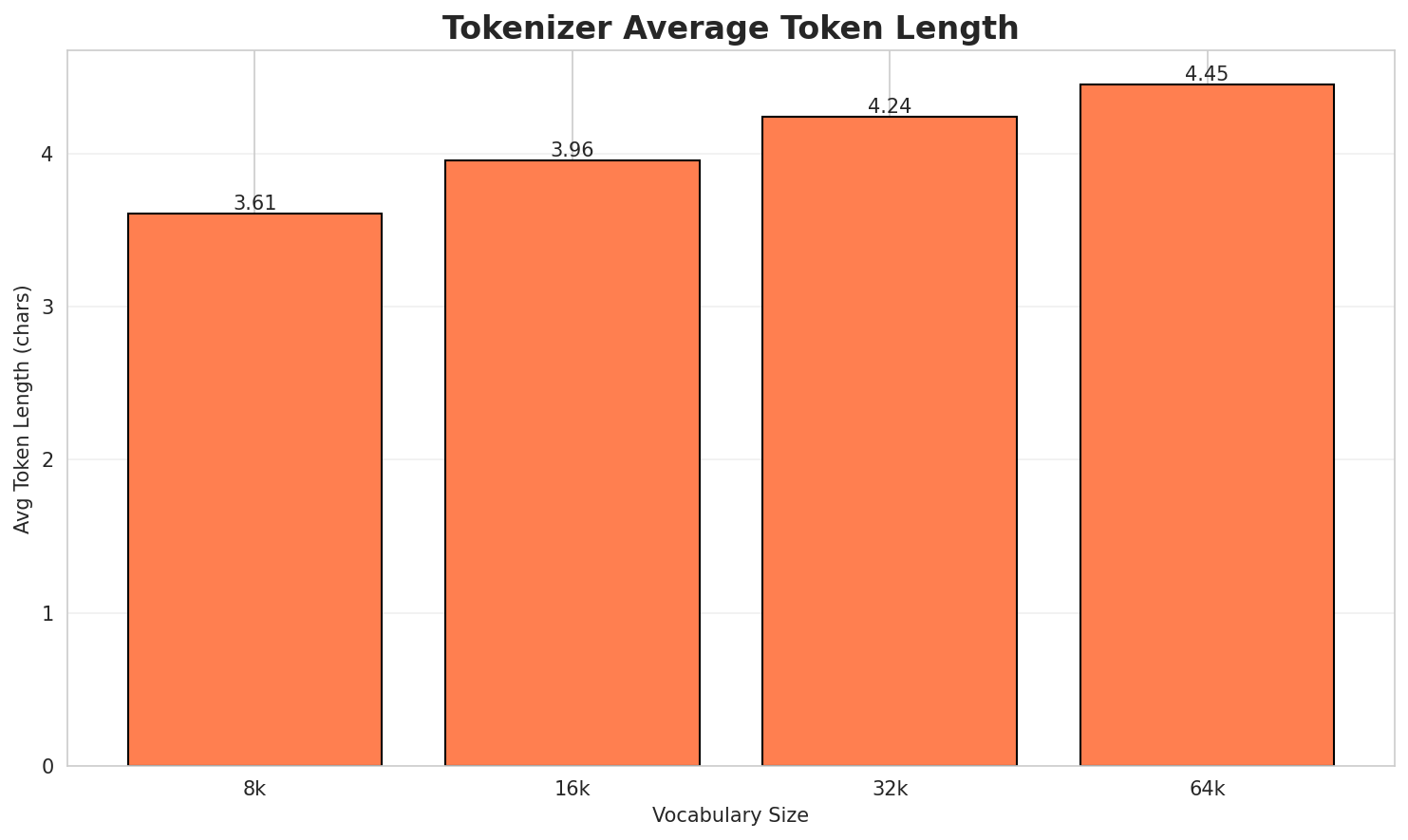
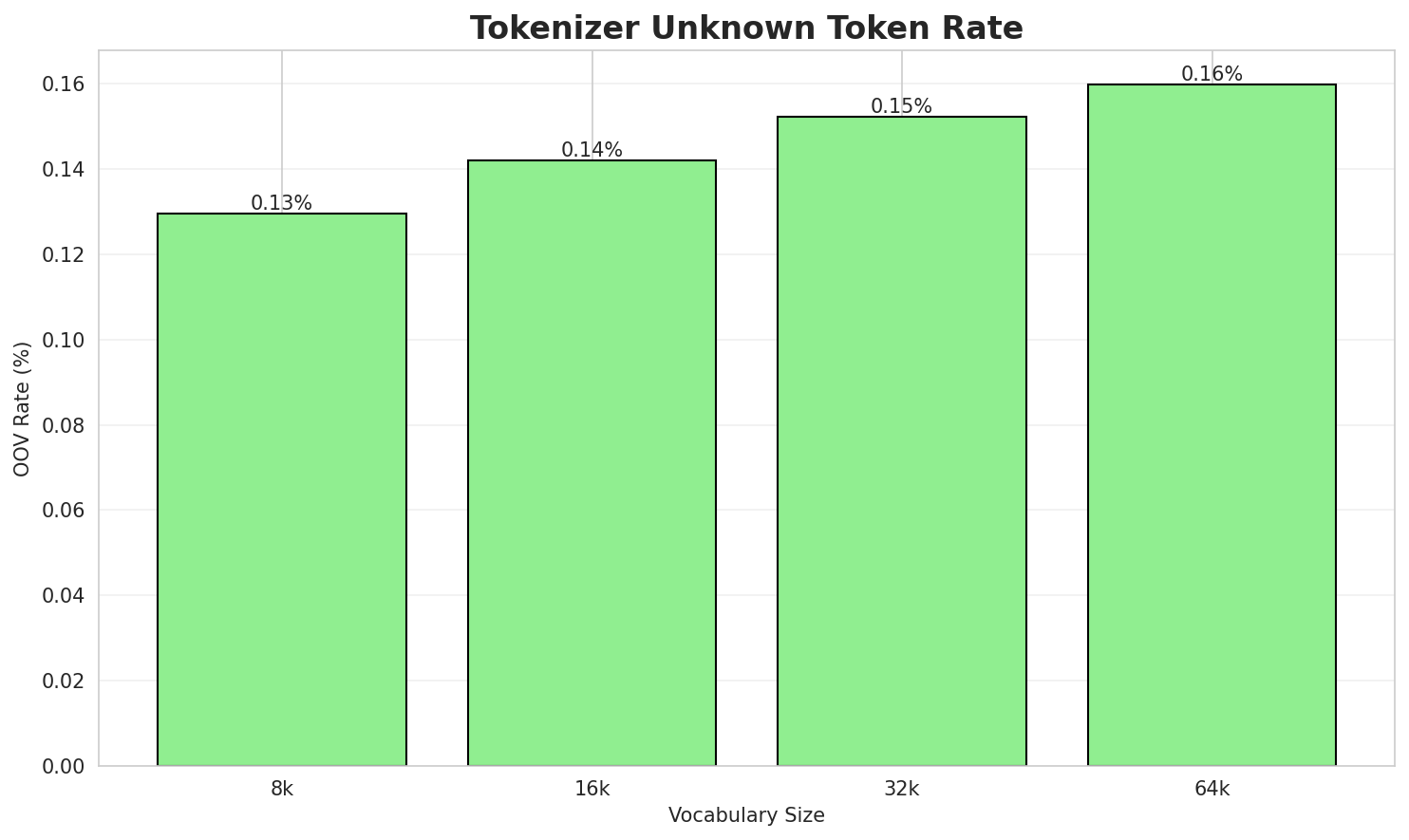
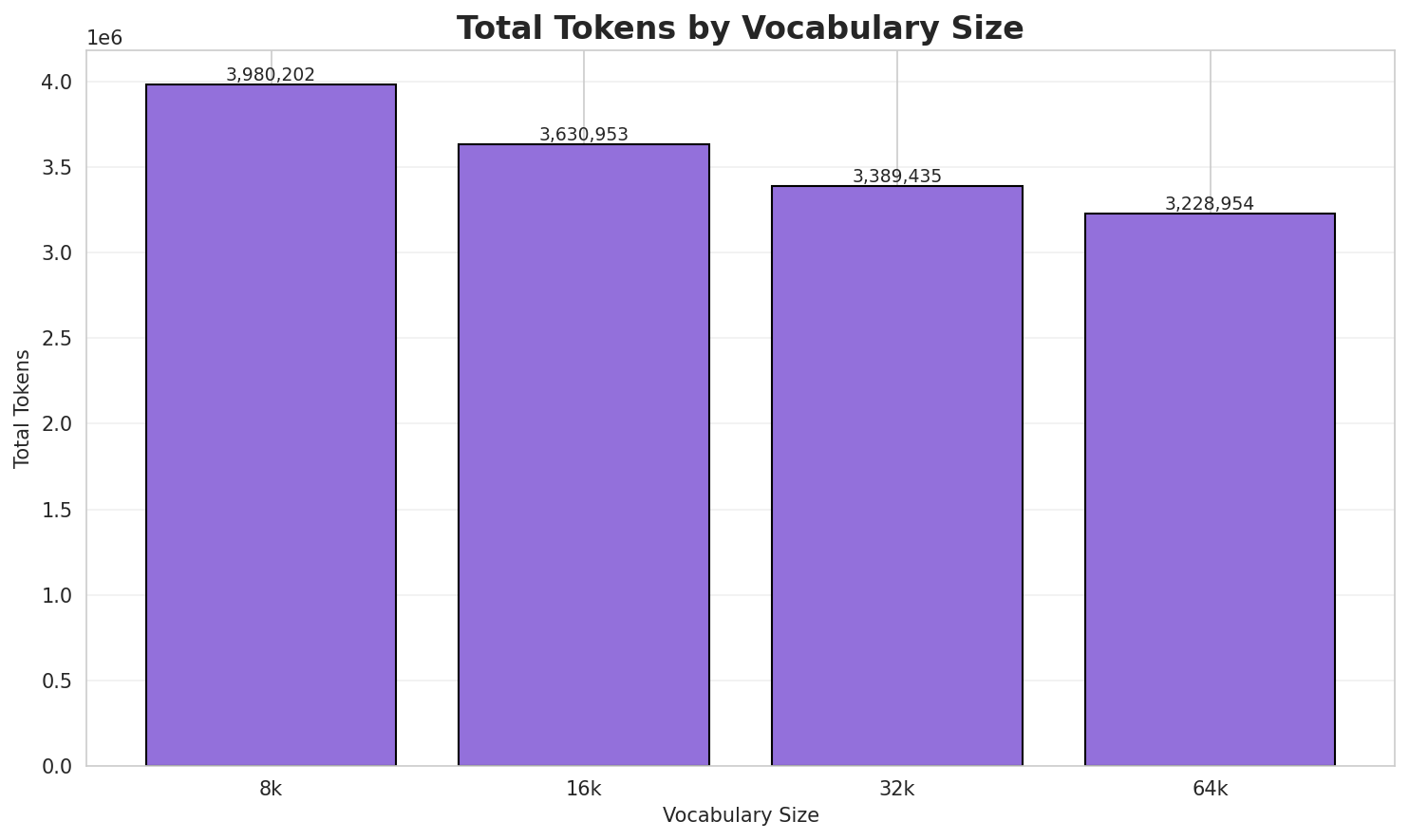
| 8k | 3.608x | 3.61 | 0.1295% | 3,980,202 |
| 16k | 3.955x | 3.96 | 0.1420% | 3,630,953 |
| 32k | 4.237x | 4.24 | 0.1521% | 3,389,435 |
| 64k | 4.448x 🏆 | 4.45 | 0.1597% | 3,228,954 |
Tokenization Examples
Below are sample sentences tokenized with each vocabulary size:
Sample 1: Llista de topònims (noms propis de lloc) del municipi de Capmany, a l'Alt Empord...
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁llista ▁de ▁topònims ▁( nom s ▁propis ▁de ▁lloc ) ... (+13 more) |
23 |
| 16k | ▁llista ▁de ▁topònims ▁( nom s ▁propis ▁de ▁lloc ) ... (+13 more) |
23 |
| 32k | ▁llista ▁de ▁topònims ▁( nom s ▁propis ▁de ▁lloc ) ... (+12 more) |
22 |
| 64k | ▁llista ▁de ▁topònims ▁( noms ▁propis ▁de ▁lloc ) ▁del ... (+10 more) |
20 |
Sample 2: Trànsportni (Krasnodar), poble del krai de Krasnodar, a Rússia Trànsportni (Maga...
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁tr àn s port ni ▁( k ras n od ... (+39 more) |
49 |
| 16k | ▁tràn sport ni ▁( k ras n od ar ), ... (+33 more) |
43 |
| 32k | ▁tràn sport ni ▁( k ras n odar ), ▁poble ... (+27 more) |
37 |
| 64k | ▁tràn sport ni ▁( k ras n odar ), ▁poble ... (+25 more) |
35 |
Sample 3: Torneigs de tennis masculí: Serbia Open (ATP 250) Belgrade Open (ATP 250) Tornei...
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁torneig s ▁de ▁ten nis ▁mascul í : ▁ser bia ... (+44 more) |
54 |
| 16k | ▁torneig s ▁de ▁tennis ▁masculí : ▁ser bia ▁open ▁( ... (+38 more) |
48 |
| 32k | ▁torneigs ▁de ▁tennis ▁masculí : ▁ser bia ▁open ▁( atp ... (+34 more) |
44 |
| 64k | ▁torneigs ▁de ▁tennis ▁masculí : ▁ser bia ▁open ▁( atp ... (+33 more) |
43 |
Key Findings
- Best Compression: 64k achieves 4.448x compression
- Lowest UNK Rate: 8k with 0.1295% unknown tokens
- Trade-off: Larger vocabularies improve compression but increase model size
- Recommendation: 32k vocabulary provides optimal balance for production use
2. N-gram Model Evaluation
Results
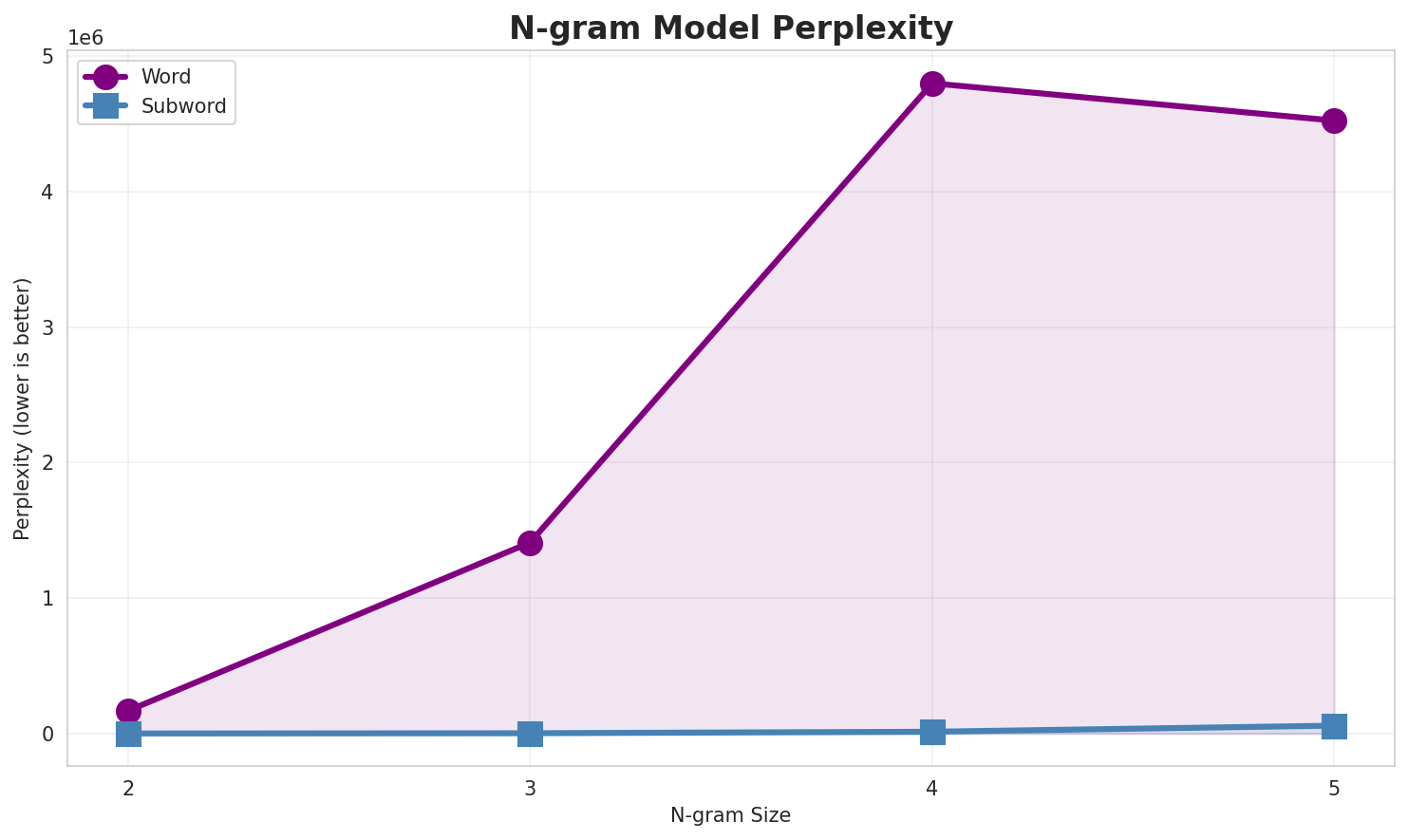
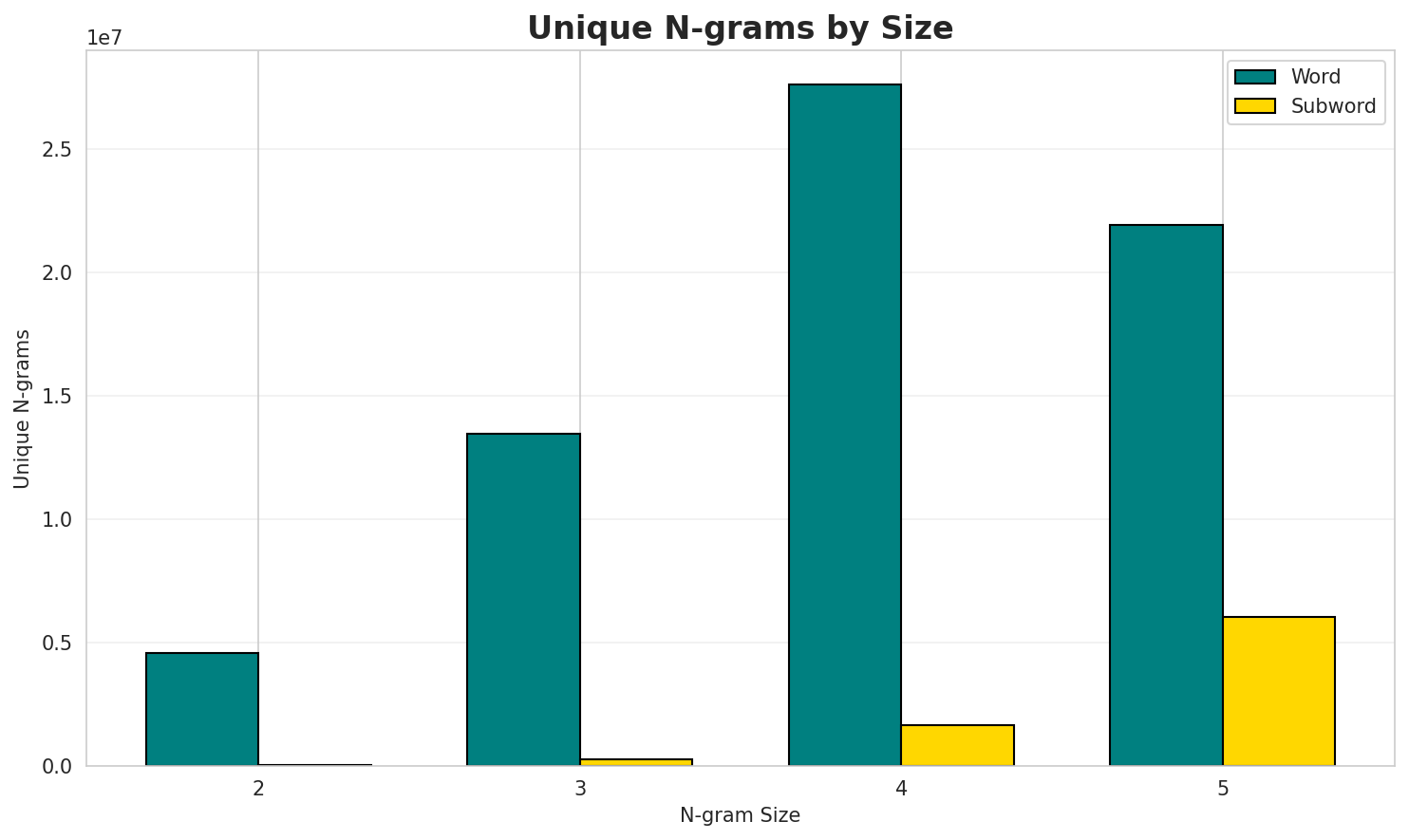
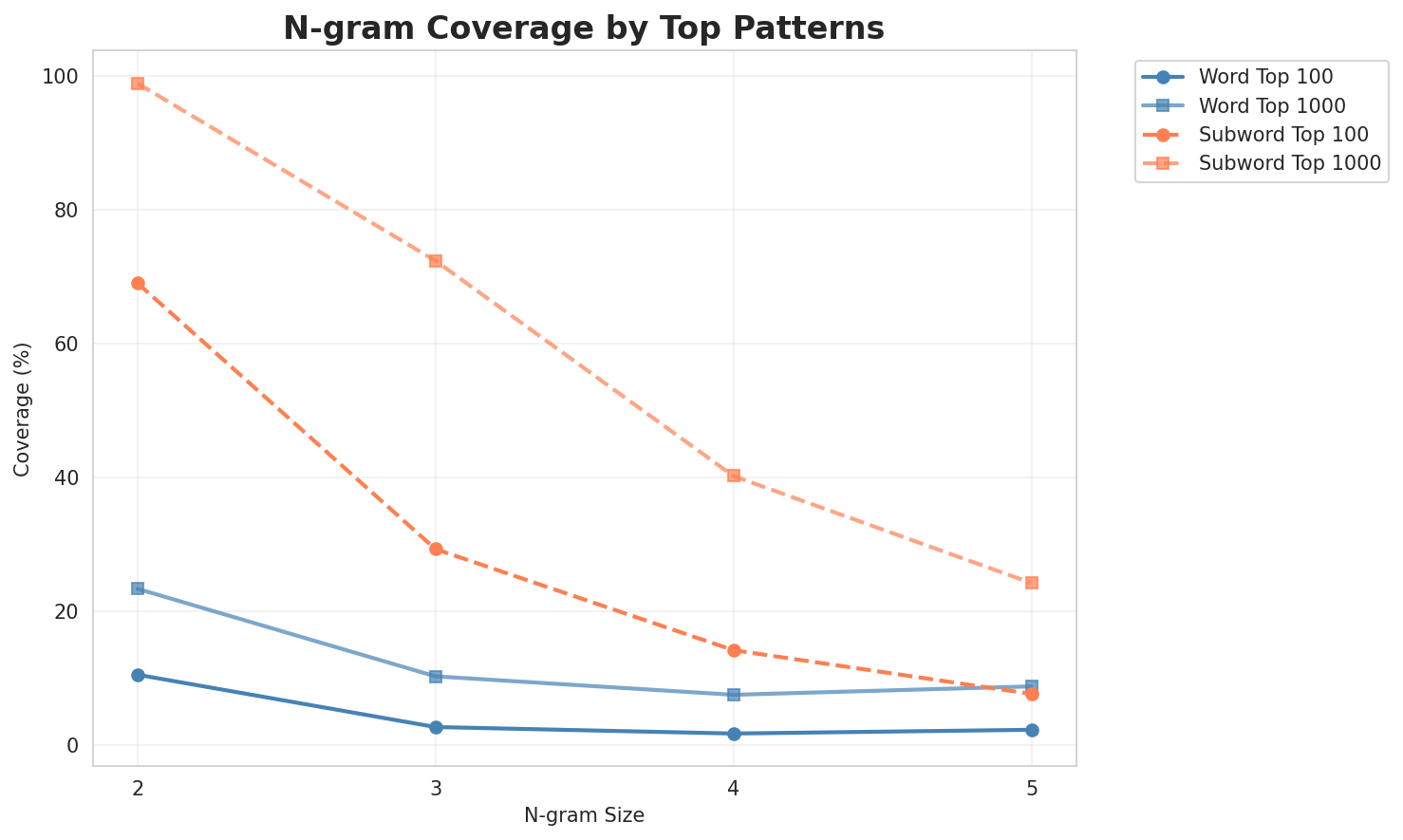
| N-gram | Variant | Perplexity | Entropy | Unique N-grams | Top-100 Coverage | Top-1000 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-gram | Word | 167,717 | 17.36 | 4,576,334 | 10.6% | 23.4% |
| 2-gram | Subword | 262 🏆 | 8.03 | 41,609 | 69.0% | 98.9% |
| 3-gram | Word | 1,409,334 | 20.43 | 13,479,698 | 2.7% | 10.3% |
| 3-gram | Subword | 2,211 | 11.11 | 288,734 | 29.3% | 72.4% |
| 4-gram | Word | 4,798,593 | 22.19 | 27,616,287 | 1.8% | 7.6% |
| 4-gram | Subword | 13,232 | 13.69 | 1,676,138 | 14.2% | 40.2% |
| 5-gram | Word | 4,523,219 | 22.11 | 21,934,897 | 2.3% | 8.8% |
| 5-gram | Subword | 58,187 | 15.83 | 6,034,155 | 7.7% | 24.2% |
Top 5 N-grams by Size
2-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | de la |
3,892,352 |
| 2 | a la |
1,832,648 |
| 3 | de l |
1,806,800 |
| 4 | a l |
1,007,338 |
| 5 | de les |
998,964 |
3-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | de la seva |
186,164 |
| 2 | per a la |
131,594 |
| 3 | referències enllaços externs |
121,418 |
| 4 | la pel lícula |
114,682 |
| 5 | d octubre de |
112,980 |
4-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | de kitt peak spacewatch |
78,569 |
| 2 | de la universitat de |
56,957 |
| 3 | que hi havia el |
55,303 |
| 4 | segons el cens del |
47,569 |
| 5 | de la família dels |
44,734 |
5-grams (Word):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | el nombre mitjà de persones |
43,284 |
| 2 | el següent diagrama mostra les |
42,548 |
| 3 | següent diagrama mostra les poblacions |
42,548 |
| 4 | diagrama mostra les poblacions més |
42,542 |
| 5 | mostra les poblacions més properes |
42,497 |
2-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | a _ |
65,660,325 |
| 2 | s _ |
52,744,093 |
| 3 | _ d |
49,682,099 |
| 4 | e _ |
42,364,044 |
| 5 | d e |
41,208,775 |
3-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | _ d e |
35,468,647 |
| 2 | d e _ |
24,280,649 |
| 3 | e s _ |
19,244,620 |
| 4 | e l _ |
15,094,409 |
| 5 | l a _ |
14,700,214 |
4-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | _ d e _ |
23,793,570 |
| 2 | _ l a _ |
12,534,324 |
| 3 | _ e l _ |
8,556,406 |
| 4 | s _ d e |
7,523,945 |
| 5 | d e _ l |
7,343,393 |
5-grams (Subword):
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | _ d e _ l |
7,323,223 |
| 2 | _ d e l _ |
5,191,709 |
| 3 | s _ d e _ |
5,107,850 |
| 4 | _ q u e _ |
4,821,740 |
| 5 | a _ d e _ |
4,540,758 |
Key Findings
- Best Perplexity: 2-gram (subword) with 262
- Entropy Trend: Decreases with larger n-grams (more predictable)
- Coverage: Top-1000 patterns cover ~24% of corpus
- Recommendation: 4-gram or 5-gram for best predictive performance
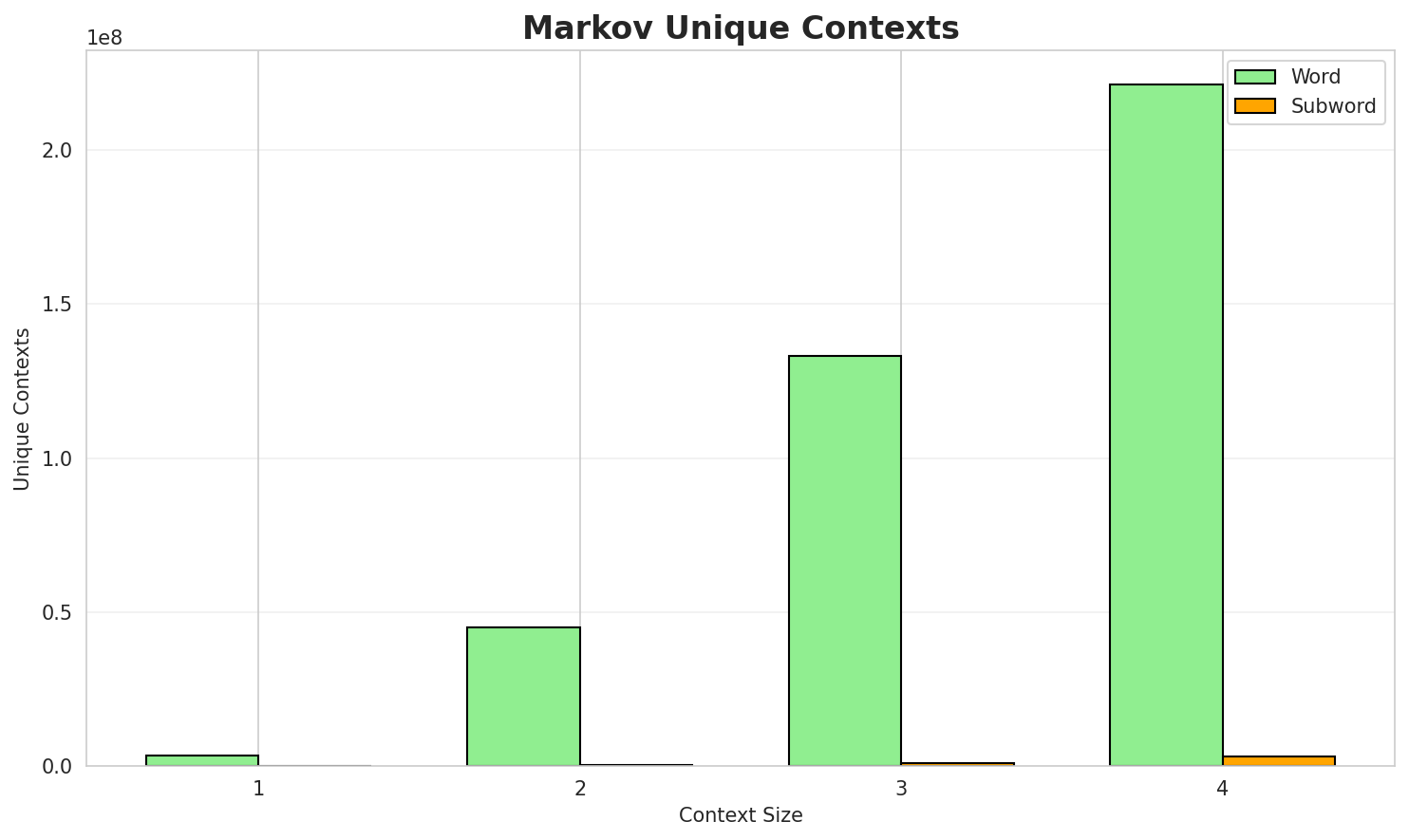
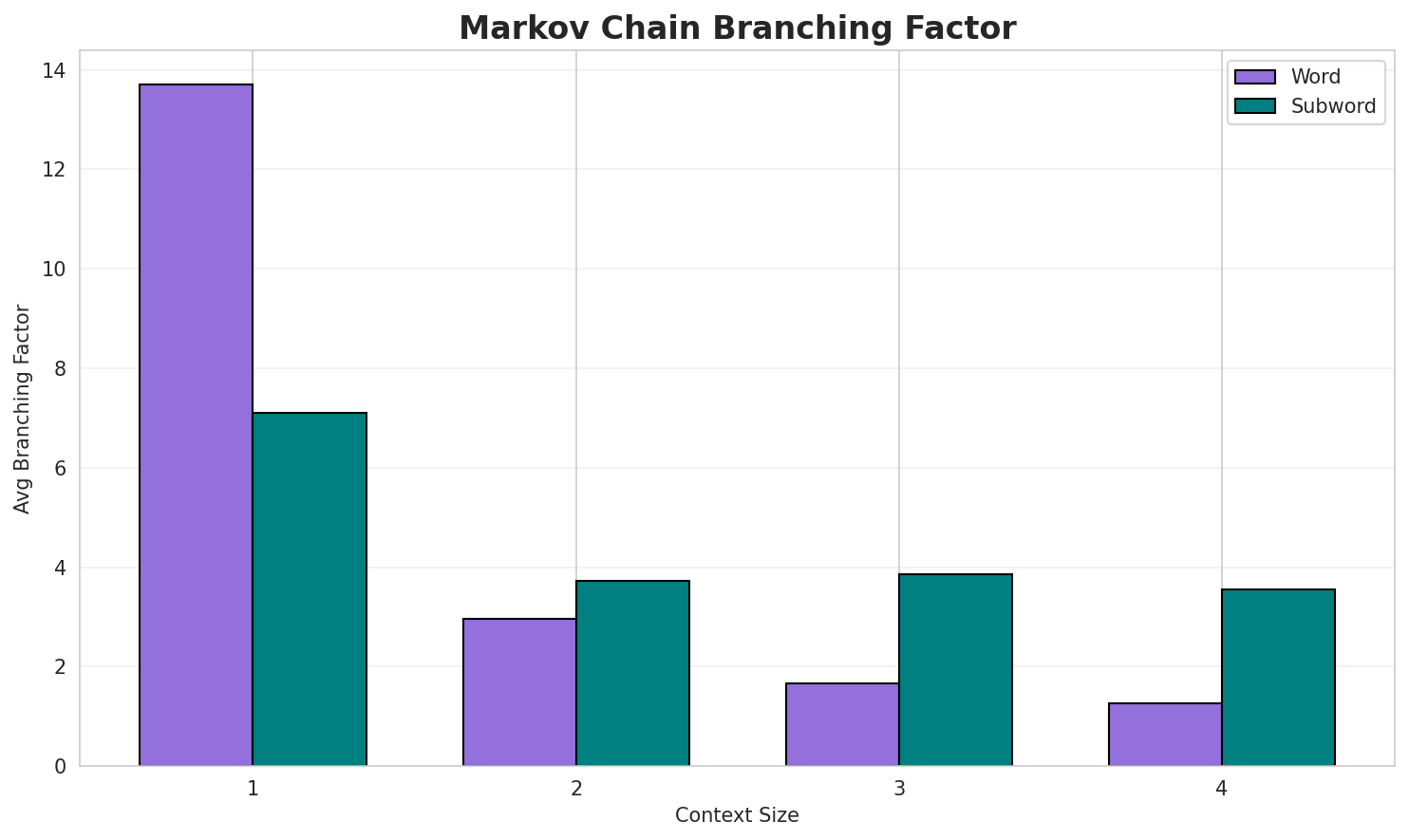
3. Markov Chain Evaluation
Results
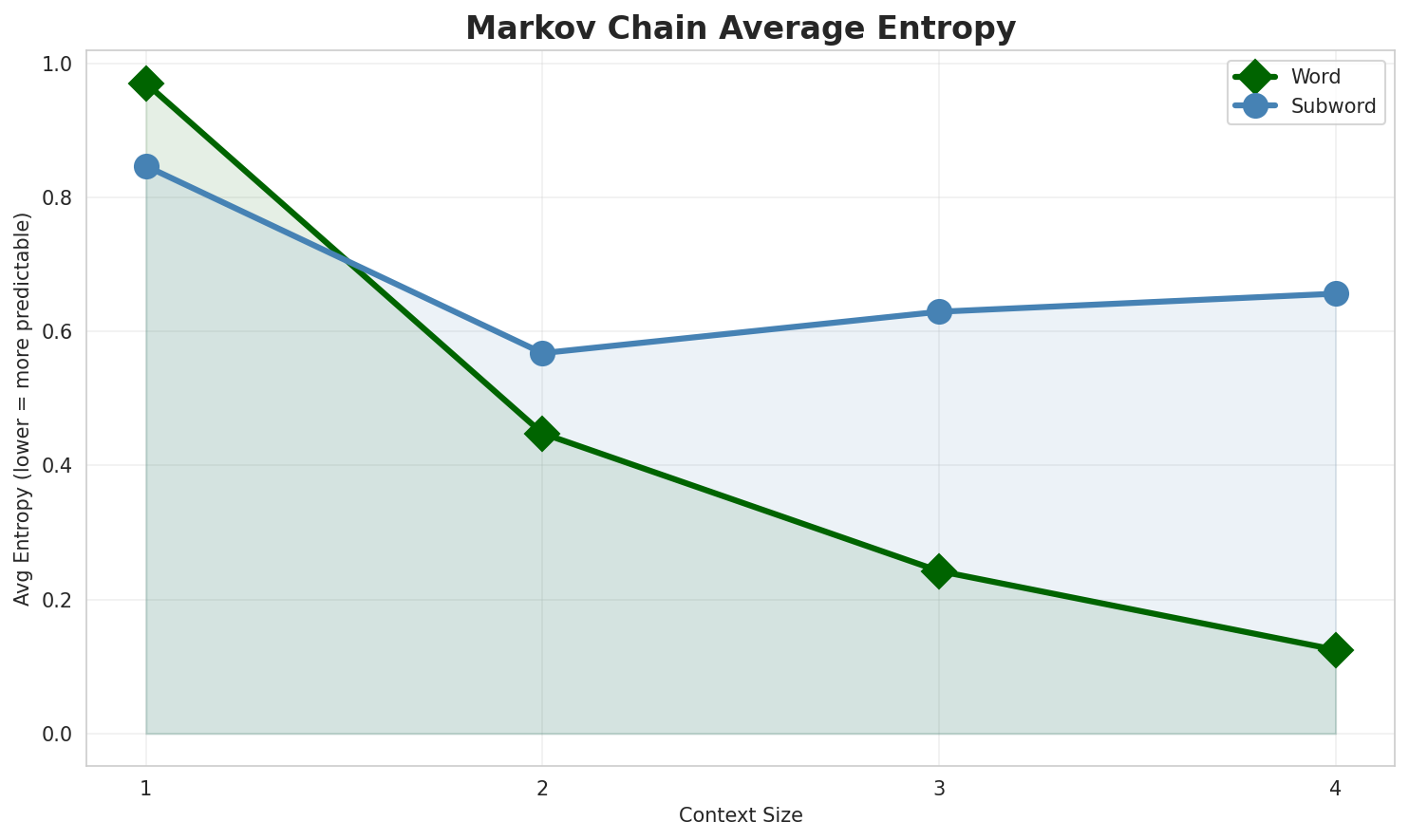
| Context | Variant | Avg Entropy | Perplexity | Branching Factor | Unique Contexts | Predictability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Word | 0.9702 | 1.959 | 13.70 | 3,298,751 | 3.0% |
| 1 | Subword | 0.8467 | 1.798 | 7.10 | 30,691 | 15.3% |
| 2 | Word | 0.4478 | 1.364 | 2.95 | 45,099,512 | 55.2% |
| 2 | Subword | 0.5676 | 1.482 | 3.72 | 217,960 | 43.2% |
| 3 | Word | 0.2425 | 1.183 | 1.66 | 133,056,441 | 75.8% |
| 3 | Subword | 0.6293 | 1.547 | 3.86 | 810,473 | 37.1% |
| 4 | Word | 0.1249 🏆 | 1.090 | 1.26 | 221,190,469 | 87.5% |
| 4 | Subword | 0.6563 | 1.576 | 3.56 | 3,128,822 | 34.4% |
Generated Text Samples (Word-based)
Below are text samples generated from each word-based Markov chain model:
Context Size 1:
de maig de la temporada l acceptació de muntar una muralla i el molí de lala població comunicació de encara que alemanya i des de la computació sent l estat substituïdai no són esmentats anteriorment icv el símbol del psoe des de guilgameix que un comerç
Context Size 2:
de la guerra di mario tronti i no solament va trobar que era del 5è al 16èa la taula de composició amb la seva història general del magistrat monetari c cassi a lade l expedició del virrei un germà gran del poble ulldeconencs o ulldeconins són coneguts com a
Context Size 3:
de la seva carrera periodística escrivint col laboracions a joves intel lectuals pertanyents a l alt...per a la secció de filosofia i ciències socials en les seves obligacions amb la seguretat i elreferències enllaços externs fira festa de la pasqua hayivky el casament vessilia o ladkannya de la ...
Context Size 4:
de kitt peak spacewatch 8 de novembre de parcak i mumford del 8 de novembre de militants del flecde la universitat de salamanca honoris causa per la universitat christian albrecht de kiel de la uni...que hi havia el 1 era una gran superfície de material de bricolatge 1 una botiga de congelats 1
Generated Text Samples (Subword-based)
Below are text samples generated from each subword-based Markov chain model:
Context Size 1:
_daral_euílere_seivinde_ditel'hiagraweros._ome_2
Context Size 2:
a_ses_va_únivencis_als_(rdor_reu_d_d'ofegria_amb_o_
Context Size 3:
_de_bre_seteodent_de_la_de_col·lociaes_pres,_nastorals
Context Size 4:
_de_doble_(a_−_batx_la_de_fan_es_va_ca_el_donar_les_si_es
Key Findings
- Best Predictability: Context-4 (word) with 87.5% predictability
- Branching Factor: Decreases with context size (more deterministic)
- Memory Trade-off: Larger contexts require more storage (3,128,822 contexts)
- Recommendation: Context-3 or Context-4 for text generation
4. Vocabulary Analysis
Statistics
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Vocabulary Size | 1,490,582 |
| Total Tokens | 372,231,757 |
| Mean Frequency | 249.72 |
| Median Frequency | 4 |
| Frequency Std Dev | 29623.92 |
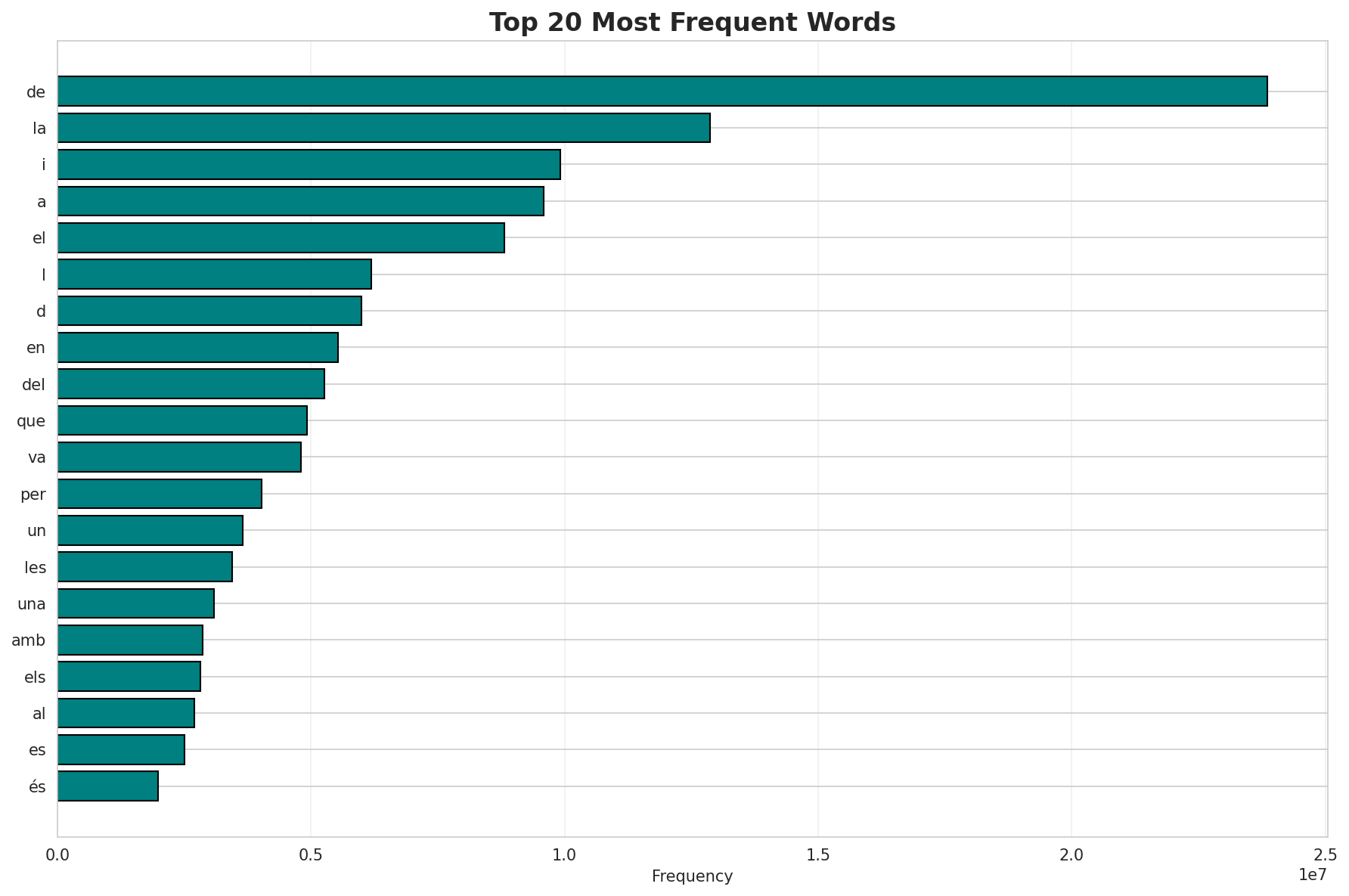
Most Common Words
| Rank | Word | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | de | 23,862,515 |
| 2 | la | 12,874,088 |
| 3 | i | 9,923,035 |
| 4 | a | 9,593,194 |
| 5 | el | 8,820,173 |
| 6 | l | 6,195,164 |
| 7 | d | 5,995,004 |
| 8 | en | 5,534,785 |
| 9 | del | 5,257,995 |
| 10 | que | 4,926,945 |
Least Common Words (from vocabulary)
| Rank | Word | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | binaritruncat | 2 |
| 2 | fanerozoiques | 2 |
| 3 | biòmers | 2 |
| 4 | nianzhi | 2 |
| 5 | fuching | 2 |
| 6 | mndm | 2 |
| 7 | cpsf | 2 |
| 8 | preestàndard | 2 |
| 9 | sweetshop | 2 |
| 10 | whakaata | 2 |
Zipf's Law Analysis
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Zipf Coefficient | 1.0222 |
| R² (Goodness of Fit) | 0.996032 |
| Adherence Quality | excellent |
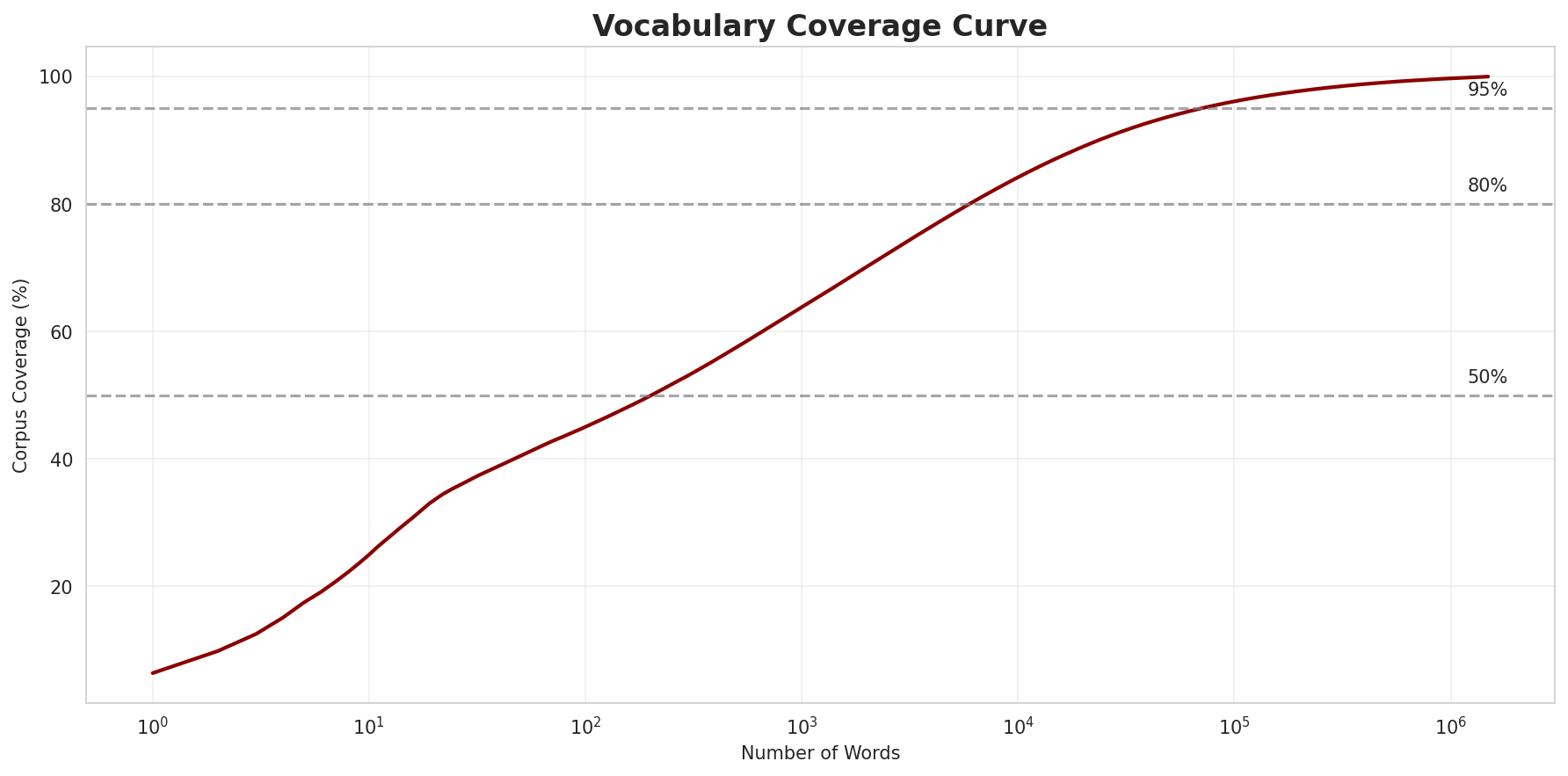
Coverage Analysis
| Top N Words | Coverage |
|---|---|
| Top 100 | 45.0% |
| Top 1,000 | 63.8% |
| Top 5,000 | 78.5% |
| Top 10,000 | 84.2% |
Key Findings
- Zipf Compliance: R²=0.9960 indicates excellent adherence to Zipf's law
- High Frequency Dominance: Top 100 words cover 45.0% of corpus
- Long Tail: 1,480,582 words needed for remaining 15.8% coverage
5. Word Embeddings Evaluation
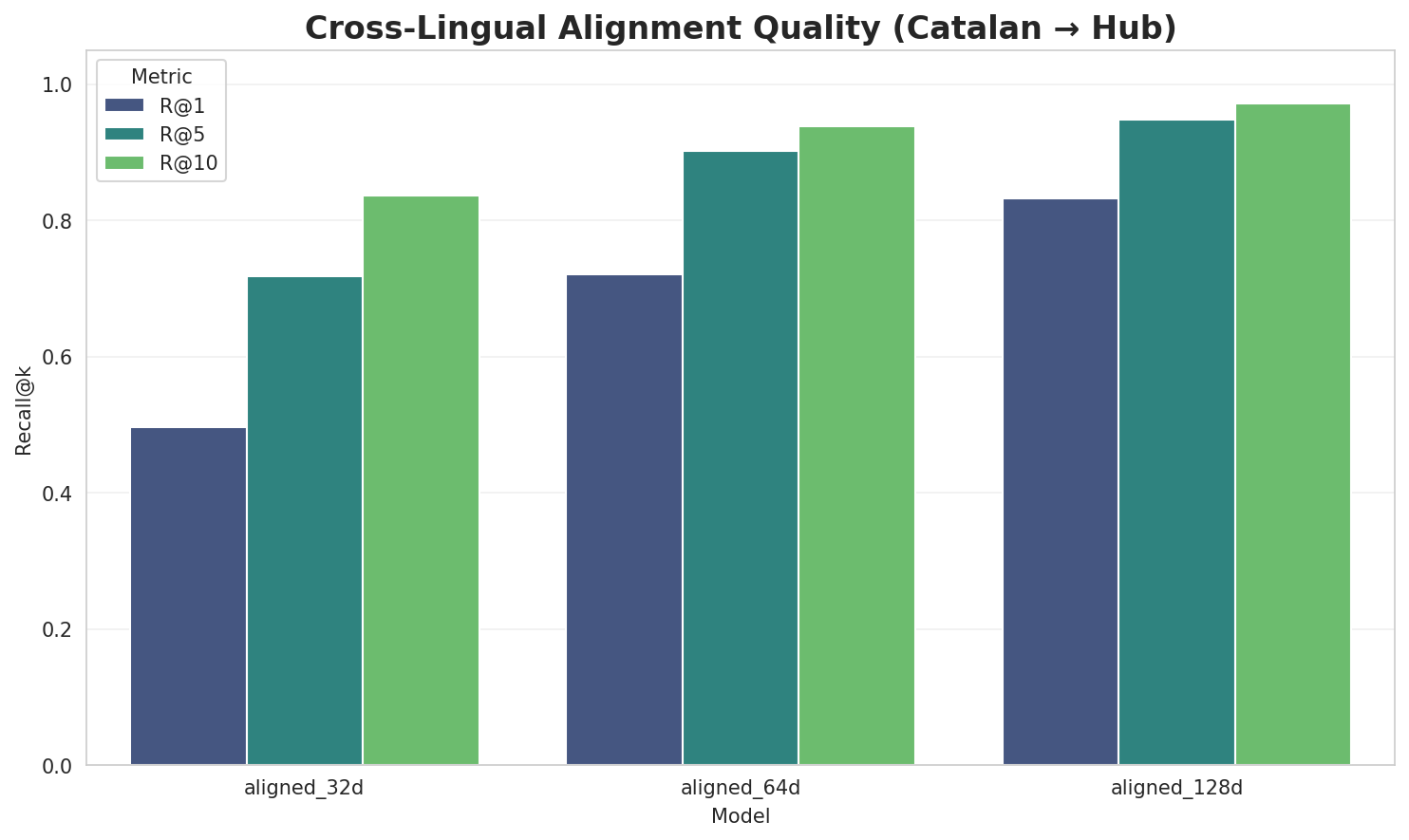
5.1 Cross-Lingual Alignment
5.2 Model Comparison
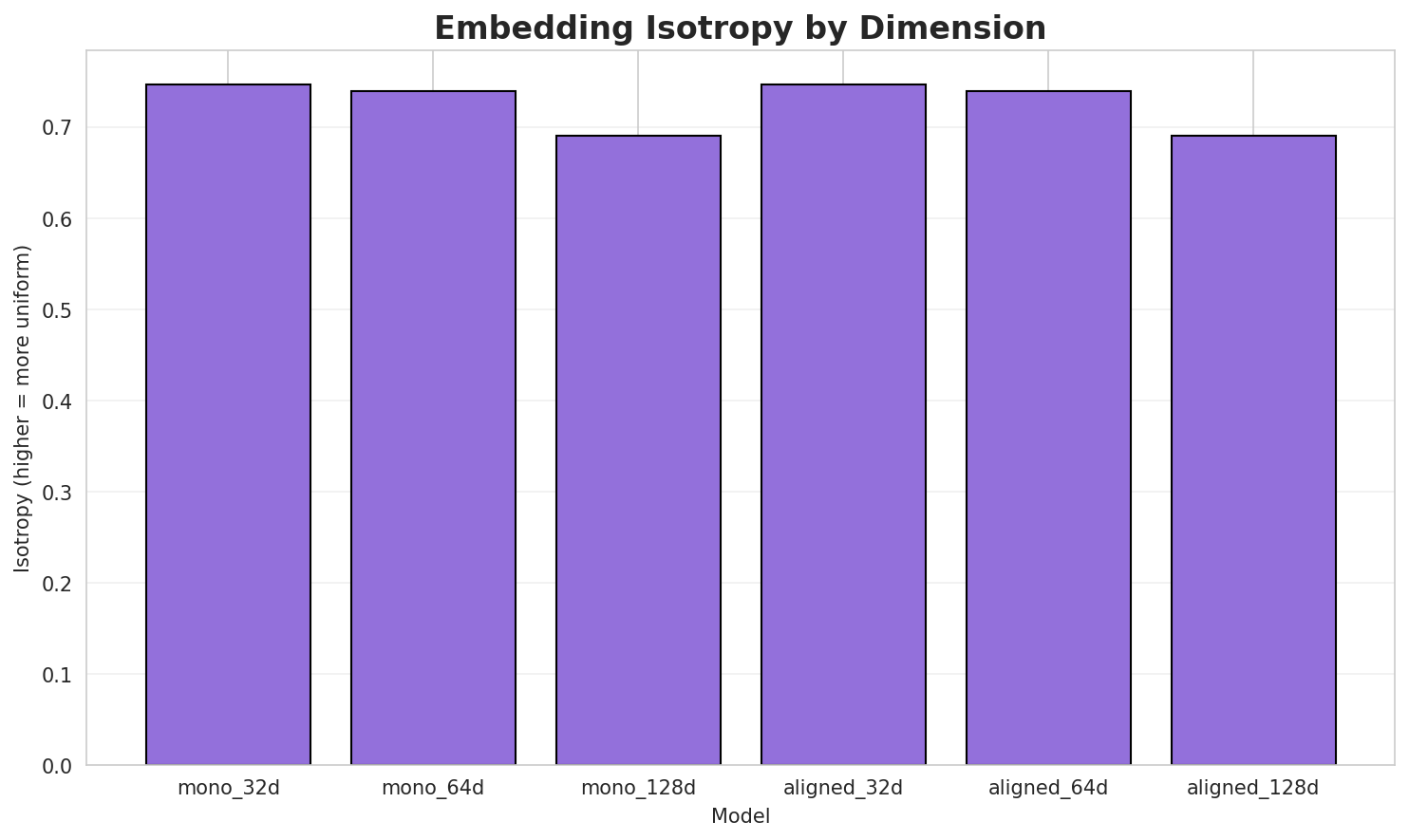
| Model | Dimension | Isotropy | Semantic Density | Alignment R@1 | Alignment R@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mono_32d | 32 | 0.7469 🏆 | 0.3896 | N/A | N/A |
| mono_64d | 64 | 0.7390 | 0.2972 | N/A | N/A |
| mono_128d | 128 | 0.6902 | 0.2374 | N/A | N/A |
| aligned_32d | 32 | 0.7469 | 0.3696 | 0.4960 | 0.8360 |
| aligned_64d | 64 | 0.7390 | 0.3068 | 0.7200 | 0.9380 |
| aligned_128d | 128 | 0.6902 | 0.2443 | 0.8320 | 0.9720 |
Key Findings
- Best Isotropy: mono_32d with 0.7469 (more uniform distribution)
- Semantic Density: Average pairwise similarity of 0.3075. Lower values indicate better semantic separation.
- Alignment Quality: Aligned models achieve up to 83.2% R@1 in cross-lingual retrieval.
- Recommendation: 128d aligned for best cross-lingual performance
6. Morphological Analysis (Experimental)
This section presents an automated morphological analysis derived from the statistical divergence between word-level and subword-level models. By analyzing where subword predictability spikes and where word-level coverage fails, we can infer linguistic structures without supervised data.
6.1 Productivity & Complexity
| Metric | Value | Interpretation | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Productivity Index | 5.000 | High morphological productivity | Reliable analysis |
| Idiomaticity Gap | -0.637 | Low formulaic content | - |
6.2 Affix Inventory (Productive Units)
These are the most productive prefixes and suffixes identified by sampling the vocabulary for global substitutability patterns. A unit is considered an affix if stripping it leaves a valid stem that appears in other contexts.
Productive Prefixes
| Prefix | Examples |
|---|---|
-ca |
canadàwilliam, cancells, callissot |
-co |
compsopogon, corlea, constitutionem |
-ma |
matricarina, masaraga, massai |
Productive Suffixes
| Suffix | Examples |
|---|---|
-s |
pomacèntrids, pentalobulars, quiotas |
-a |
matricarina, arduinna, yarima |
-es |
asfèriques, biomatemàtiques, quies |
-en |
grieneisen, robien, tensionen |
-is |
rufistrigalis, reaccionaris, catàrsis |
-ia |
praskóvia, llògia, orogenia |
-ta |
lucasta, samudragupta, lisetita |
6.3 Bound Stems (Lexical Roots)
Bound stems are high-frequency subword units that are semantically cohesive but rarely appear as standalone words. These often correspond to the 'core' of a word that requires inflection or derivation to be valid.
| Stem | Cohesion | Substitutability | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
nter |
1.39x | 729 contexts | inter, anter, únter |
efer |
1.66x | 177 contexts | kefer, lefer, defer |
uerr |
1.61x | 153 contexts | uerra, guerr, duerr |
espr |
1.73x | 95 contexts | esprî, despr, esprai |
stru |
1.32x | 389 contexts | strum, struk, strus |
rson |
1.46x | 205 contexts | rsona, arson, urson |
ient |
1.31x | 364 contexts | rient, oient, lient |
lmen |
1.57x | 122 contexts | ulmen, ilmen, olmen |
rinc |
1.48x | 147 contexts | rinck, rincó, rinca |
ènci |
1.57x | 107 contexts | ència, mència, lència |
embr |
1.33x | 234 contexts | membr, embre, embry |
onst |
1.42x | 159 contexts | onsta, konst, const |
6.4 Affix Compatibility (Co-occurrence)
This table shows which prefixes and suffixes most frequently co-occur on the same stems, revealing the 'stacking' rules of the language's morphology.
| Prefix | Suffix | Frequency | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
-co |
-s |
48 words | conventos, conservadors |
-ma |
-a |
45 words | masicka, macclureana |
-ca |
-s |
40 words | callolepis, cambyses |
-co |
-a |
35 words | comunera, costanzana |
-ma |
-s |
33 words | mahates, maktens |
-ca |
-a |
30 words | camborda, cardellina |
-co |
-es |
14 words | congoatlàntiques, colomates |
-ca |
-es |
11 words | cambyses, calcídies |
-ma |
-es |
9 words | mahates, masies |
-ma |
-ta |
9 words | magnesiodumortierita, malwatta |
6.5 Recursive Morpheme Segmentation
Using Recursive Hierarchical Substitutability, we decompose complex words into their constituent morphemes. This approach handles nested affixes (e.g., prefix-prefix-root-suffix).
| Word | Suggested Split | Confidence | Stem |
|---|---|---|---|
| guerrista | guerr-is-ta |
6.0 | guerr |
| whitlockita | whitlocki-ta |
4.5 | whitlocki |
| assumptionis | assumption-is |
4.5 | assumption |
| zumacales | zumacal-es |
4.5 | zumacal |
| raperswilen | raperswil-en |
4.5 | raperswil |
| antinomies | antinomi-es |
4.5 | antinomi |
| reglamentaren | reglamentar-en |
4.5 | reglamentar |
| remarcaria | remarcar-ia |
4.5 | remarcar |
| reichsfürsten | reichsfürst-en |
4.5 | reichsfürst |
| deflectores | deflector-es |
4.5 | deflector |
| produeixen | produeix-en |
4.5 | produeix |
| autoadjuntes | autoadjunt-es |
4.5 | autoadjunt |
| subministraria | subministrar-ia |
4.5 | subministrar |
| barbertonita | barbertoni-ta |
4.5 | barbertoni |
| balsameres | balsamer-es |
4.5 | balsamer |
6.6 Linguistic Interpretation
Automated Insight: The language Catalan shows high morphological productivity. The subword models are significantly more efficient than word models, suggesting a rich system of affixation or compounding.
7. Summary & Recommendations
Production Recommendations
| Component | Recommended | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Tokenizer | 64k BPE | Best compression (4.45x) |
| N-gram | 2-gram | Lowest perplexity (262) |
| Markov | Context-4 | Highest predictability (87.5%) |
| Embeddings | 100d | Balanced semantic capture and isotropy |
Appendix: Metrics Glossary & Interpretation Guide
This section provides definitions, intuitions, and guidance for interpreting the metrics used throughout this report.
Tokenizer Metrics
Compression Ratio
Definition: The ratio of characters to tokens (chars/token). Measures how efficiently the tokenizer represents text.
Intuition: Higher compression means fewer tokens needed to represent the same text, reducing sequence lengths for downstream models. A 3x compression means ~3 characters per token on average.
What to seek: Higher is generally better for efficiency, but extremely high compression may indicate overly aggressive merging that loses morphological information.
Average Token Length (Fertility)
Definition: Mean number of characters per token produced by the tokenizer.
Intuition: Reflects the granularity of tokenization. Longer tokens capture more context but may struggle with rare words; shorter tokens are more flexible but increase sequence length.
What to seek: Balance between 2-5 characters for most languages. Arabic/morphologically-rich languages may benefit from slightly longer tokens.
Unknown Token Rate (OOV Rate)
Definition: Percentage of tokens that map to the unknown/UNK token, indicating words the tokenizer cannot represent.
Intuition: Lower OOV means better vocabulary coverage. High OOV indicates the tokenizer encounters many unseen character sequences.
What to seek: Below 1% is excellent; below 5% is acceptable. BPE tokenizers typically achieve very low OOV due to subword fallback.
N-gram Model Metrics
Perplexity
Definition: Measures how "surprised" the model is by test data. Mathematically: 2^(cross-entropy). Lower values indicate better prediction.
Intuition: If perplexity is 100, the model is as uncertain as if choosing uniformly among 100 options at each step. A perplexity of 10 means effectively choosing among 10 equally likely options.
What to seek: Lower is better. Perplexity decreases with larger n-grams (more context). Values vary widely by language and corpus size.
Entropy
Definition: Average information content (in bits) needed to encode the next token given the context. Related to perplexity: perplexity = 2^entropy.
Intuition: High entropy means high uncertainty/randomness; low entropy means predictable patterns. Natural language typically has entropy between 1-4 bits per character.
What to seek: Lower entropy indicates more predictable text patterns. Entropy should decrease as n-gram size increases.
Coverage (Top-K)
Definition: Percentage of corpus occurrences explained by the top K most frequent n-grams.
Intuition: High coverage with few patterns indicates repetitive/formulaic text; low coverage suggests diverse vocabulary usage.
What to seek: Depends on use case. For language modeling, moderate coverage (40-60% with top-1000) is typical for natural text.
Markov Chain Metrics
Average Entropy
Definition: Mean entropy across all contexts, measuring average uncertainty in next-word prediction.
Intuition: Lower entropy means the model is more confident about what comes next. Context-1 has high entropy (many possible next words); Context-4 has low entropy (few likely continuations).
What to seek: Decreasing entropy with larger context sizes. Very low entropy (<0.1) indicates highly deterministic transitions.
Branching Factor
Definition: Average number of unique next tokens observed for each context.
Intuition: High branching = many possible continuations (flexible but uncertain); low branching = few options (predictable but potentially repetitive).
What to seek: Branching factor should decrease with context size. Values near 1.0 indicate nearly deterministic chains.
Predictability
Definition: Derived metric: (1 - normalized_entropy) × 100%. Indicates how deterministic the model's predictions are.
Intuition: 100% predictability means the next word is always certain; 0% means completely random. Real text falls between these extremes.
What to seek: Higher predictability for text generation quality, but too high (>98%) may produce repetitive output.
Vocabulary & Zipf's Law Metrics
Zipf's Coefficient
Definition: The slope of the log-log plot of word frequency vs. rank. Zipf's law predicts this should be approximately -1.
Intuition: A coefficient near -1 indicates the corpus follows natural language patterns where a few words are very common and most words are rare.
What to seek: Values between -0.8 and -1.2 indicate healthy natural language distribution. Deviations may suggest domain-specific or artificial text.
R² (Coefficient of Determination)
Definition: Measures how well the linear fit explains the frequency-rank relationship. Ranges from 0 to 1.
Intuition: R² near 1.0 means the data closely follows Zipf's law; lower values indicate deviation from expected word frequency patterns.
What to seek: R² > 0.95 is excellent; > 0.99 indicates near-perfect Zipf adherence typical of large natural corpora.
Vocabulary Coverage
Definition: Cumulative percentage of corpus tokens accounted for by the top N words.
Intuition: Shows how concentrated word usage is. If top-100 words cover 50% of text, the corpus relies heavily on common words.
What to seek: Top-100 covering 30-50% is typical. Higher coverage indicates more repetitive text; lower suggests richer vocabulary.
Word Embedding Metrics
Isotropy
Definition: Measures how uniformly distributed vectors are in the embedding space. Computed as the ratio of minimum to maximum singular values.
Intuition: High isotropy (near 1.0) means vectors spread evenly in all directions; low isotropy means vectors cluster in certain directions, reducing expressiveness.
What to seek: Higher isotropy generally indicates better-quality embeddings. Values > 0.1 are reasonable; > 0.3 is good. Lower-dimensional embeddings tend to have higher isotropy.
Average Norm
Definition: Mean magnitude (L2 norm) of word vectors in the embedding space.
Intuition: Indicates the typical "length" of vectors. Consistent norms suggest stable training; high variance may indicate some words are undertrained.
What to seek: Relatively consistent norms across models. The absolute value matters less than consistency (low std deviation).
Cosine Similarity
Definition: Measures angular similarity between vectors, ranging from -1 (opposite) to 1 (identical direction).
Intuition: Words with similar meanings should have high cosine similarity. This is the standard metric for semantic relatedness in embeddings.
What to seek: Semantically related words should score > 0.5; unrelated words should be near 0. Synonyms often score > 0.7.
t-SNE Visualization
Definition: t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding - a dimensionality reduction technique that preserves local structure for visualization.
Intuition: Clusters in t-SNE plots indicate groups of semantically related words. Spread indicates vocabulary diversity; tight clusters suggest semantic coherence.
What to seek: Meaningful clusters (e.g., numbers together, verbs together). Avoid over-interpreting distances - t-SNE preserves local, not global, structure.
General Interpretation Guidelines
- Compare within model families: Metrics are most meaningful when comparing models of the same type (e.g., 8k vs 64k tokenizer).
- Consider trade-offs: Better performance on one metric often comes at the cost of another (e.g., compression vs. OOV rate).
- Context matters: Optimal values depend on downstream tasks. Text generation may prioritize different metrics than classification.
- Corpus influence: All metrics are influenced by corpus characteristics. Wikipedia text differs from social media or literature.
- Language-specific patterns: Morphologically rich languages (like Arabic) may show different optimal ranges than analytic languages.
Visualizations Index
| Visualization | Description |
|---|---|
| Tokenizer Compression | Compression ratios by vocabulary size |
| Tokenizer Fertility | Average token length by vocabulary |
| Tokenizer OOV | Unknown token rates |
| Tokenizer Total Tokens | Total tokens by vocabulary |
| N-gram Perplexity | Perplexity by n-gram size |
| N-gram Entropy | Entropy by n-gram size |
| N-gram Coverage | Top pattern coverage |
| N-gram Unique | Unique n-gram counts |
| Markov Entropy | Entropy by context size |
| Markov Branching | Branching factor by context |
| Markov Contexts | Unique context counts |
| Zipf's Law | Frequency-rank distribution with fit |
| Vocab Frequency | Word frequency distribution |
| Top 20 Words | Most frequent words |
| Vocab Coverage | Cumulative coverage curve |
| Embedding Isotropy | Vector space uniformity |
| Embedding Norms | Vector magnitude distribution |
| Embedding Similarity | Word similarity heatmap |
| Nearest Neighbors | Similar words for key terms |
| t-SNE Words | 2D word embedding visualization |
| t-SNE Sentences | 2D sentence embedding visualization |
| Position Encoding | Encoding method comparison |
| Model Sizes | Storage requirements |
| Performance Dashboard | Comprehensive performance overview |
About This Project
Data Source
Models trained on wikipedia-monthly - a monthly snapshot of Wikipedia articles across 300+ languages.
Project
A project by Wikilangs - Open-source NLP models for every Wikipedia language.
Maintainer
Citation
If you use these models in your research, please cite:
@misc{wikilangs2025,
author = {Kamali, Omar},
title = {Wikilangs: Open NLP Models for Wikipedia Languages},
year = {2025},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.18073153},
publisher = {Zenodo},
url = {https://huggingface.co/wikilangs}
institution = {Omneity Labs}
}
License
MIT License - Free for academic and commercial use.
Links
- 🌐 Website: wikilangs.org
- 🤗 Models: huggingface.co/wikilangs
- 📊 Data: wikipedia-monthly
- 👤 Author: Omar Kamali
- 🤝 Sponsor: Featherless AI
Generated by Wikilangs Models Pipeline
Report Date: 2026-01-08 03:10:53