Quantum Assistant: Specialization of Multimodal Models for Quantum Computing
Model Description
This model is a fine-tuned version of Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct specialized for quantum computing tasks using Qiskit 2.0. This model can interpret visual representations of quantum computing: circuit diagrams, Bloch spheres, and measurement histograms.
The model was trained using DoRA (Weight-Decomposed Low-Rank Adaptation) with rank 16 for 1 epoch on the Quantum Assistant Dataset. DoRA decomposes weights into magnitude and direction components. This model was part of the Phase 1 PEFT comparison experiments and was not evaluated on external benchmarks.
Key Capabilities
- Code Generation: Generate complete Qiskit code from natural language descriptions
- Function Completion: Complete function bodies from signatures and docstrings
- Visual Understanding: Interpret quantum circuit diagrams, Bloch spheres, and histograms
- Conceptual Explanations: Answer questions about quantum computing theory
- Qiskit 2.0 Compliant: Uses modern APIs (SamplerV2, EstimatorV2, generate_preset_pass_manager)
Training Evaluation
This model was part of the Phase 1 PEFT variant comparison experiments. It was not evaluated on external benchmarks (Qiskit HumanEval, Qiskit HumanEval Hard, or synthetic test set).
Internal Validation Metrics
| Metric | Value | Step |
|---|---|---|
| Eval Loss | 0.622 | 183 (final) |
| Eval Token Accuracy | 0.818 | 183 (final) |
| Train Loss | 0.605 | 183 (final) |
| Train Token Accuracy | 0.828 | 183 (final) |
| Training Runtime | 2,307 seconds (~38.5 min) | 1 epoch |
PEFT Comparison Analysis
DoRA achieved equivalent performance to rsLoRA (Eval Loss 0.622) in Phase 1 experiments:
- Performance matched rsLoRA (both achieved 0.622 eval loss, 0.818 accuracy)
- 2.18× computational overhead compared to rsLoRA (2,307s vs 1,060s)
- Slower due to magnitude-direction decomposition in each forward pass
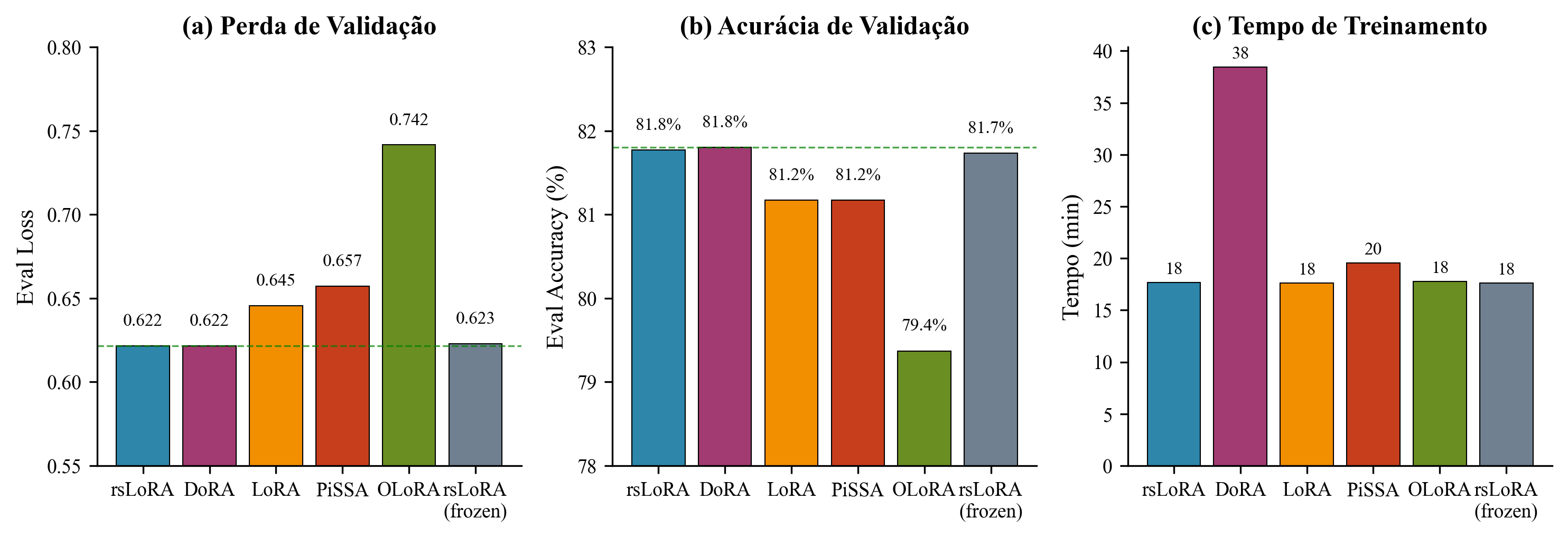
Comparison of PEFT variants: (a) validation loss, (b) token accuracy, (c) training time
Conclusion: While DoRA matches rsLoRA in final performance, the significant computational overhead without performance gains makes rsLoRA the preferred choice for efficiency.
Training Strategy
The experimental strategy was organized in two phases: PEFT technique selection and hyperparameter optimization.
Phase 1: PEFT Variant Comparison
Five LoRA variants were compared with controlled configuration (r=16, α=32, 1 epoch):
| Variant | Eval Loss ↓ | Eval Accuracy ↑ | Runtime (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| rsLoRA | 0.622 | 0.818 | 1,060 |
| DoRA | 0.622 | 0.818 | 2,307 |
| rsLoRA (frozen aligner) | 0.623 | 0.817 | 1,057 |
| LoRA (vanilla) | 0.646 | 0.812 | 1,056 |
| PiSSA | 0.657 | 0.812 | 1,172 |
| OLoRA | 0.742 | 0.794 | 1,067 |

Comparison of PEFT variants: (a) validation loss, (b) token accuracy, (c) training time
Key findings:
- rsLoRA and DoRA achieved equivalent performance (Eval Loss 0.622)
- DoRA has 2.18× computational overhead (2,307s vs 1,060s) due to magnitude-direction decomposition
- rsLoRA selected for optimal performance-efficiency trade-off
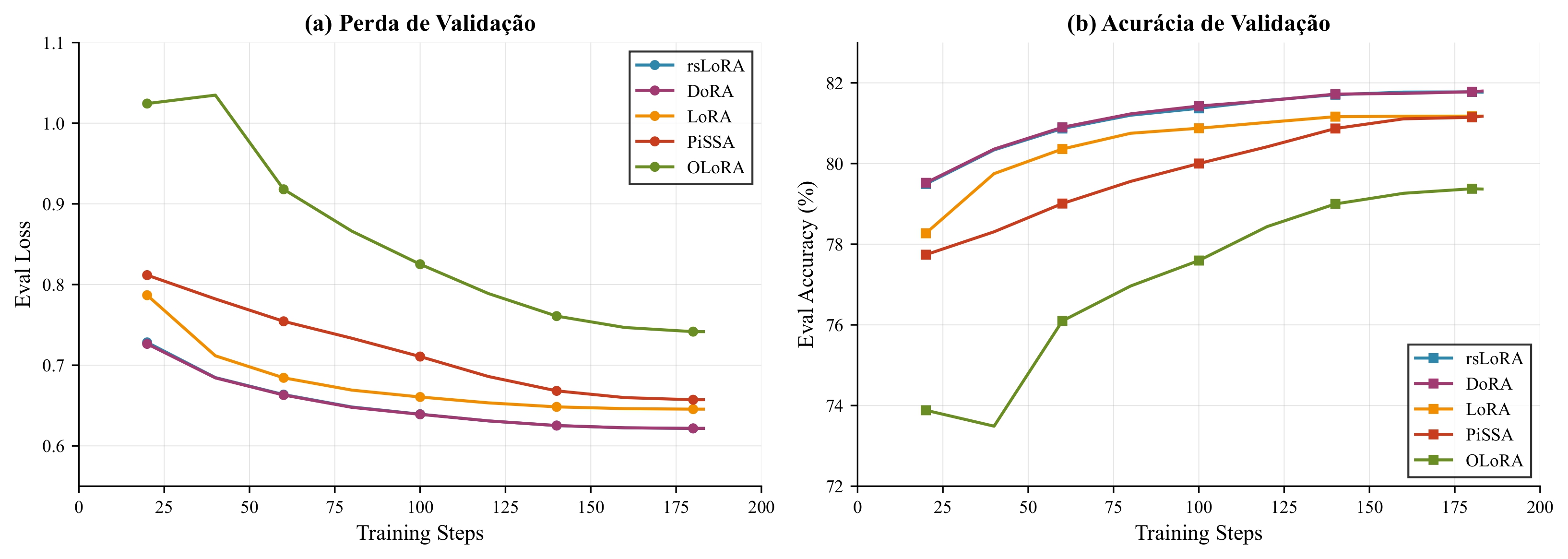
Convergence curves of validation loss for PEFT variants
Phase 2: Rank and Epoch Optimization
With rsLoRA selected, the impact of adapter rank and training duration was investigated:
| Configuration | Eval Loss ↓ | Eval Accuracy ↑ | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| r=32, 1 epoch | 0.607 | 0.821 | Optimal trade-off |
| r=64, 1 epoch | 0.609 | 0.822 | Marginal improvement |
| r=16, 1 epoch | 0.622 | 0.818 | Baseline rsLoRA |
| r=32, 2 epochs | 0.638 | 0.825 | Slight overfitting |
| r=128, 3 epochs | 0.789 | 0.822 | Severe overfitting |
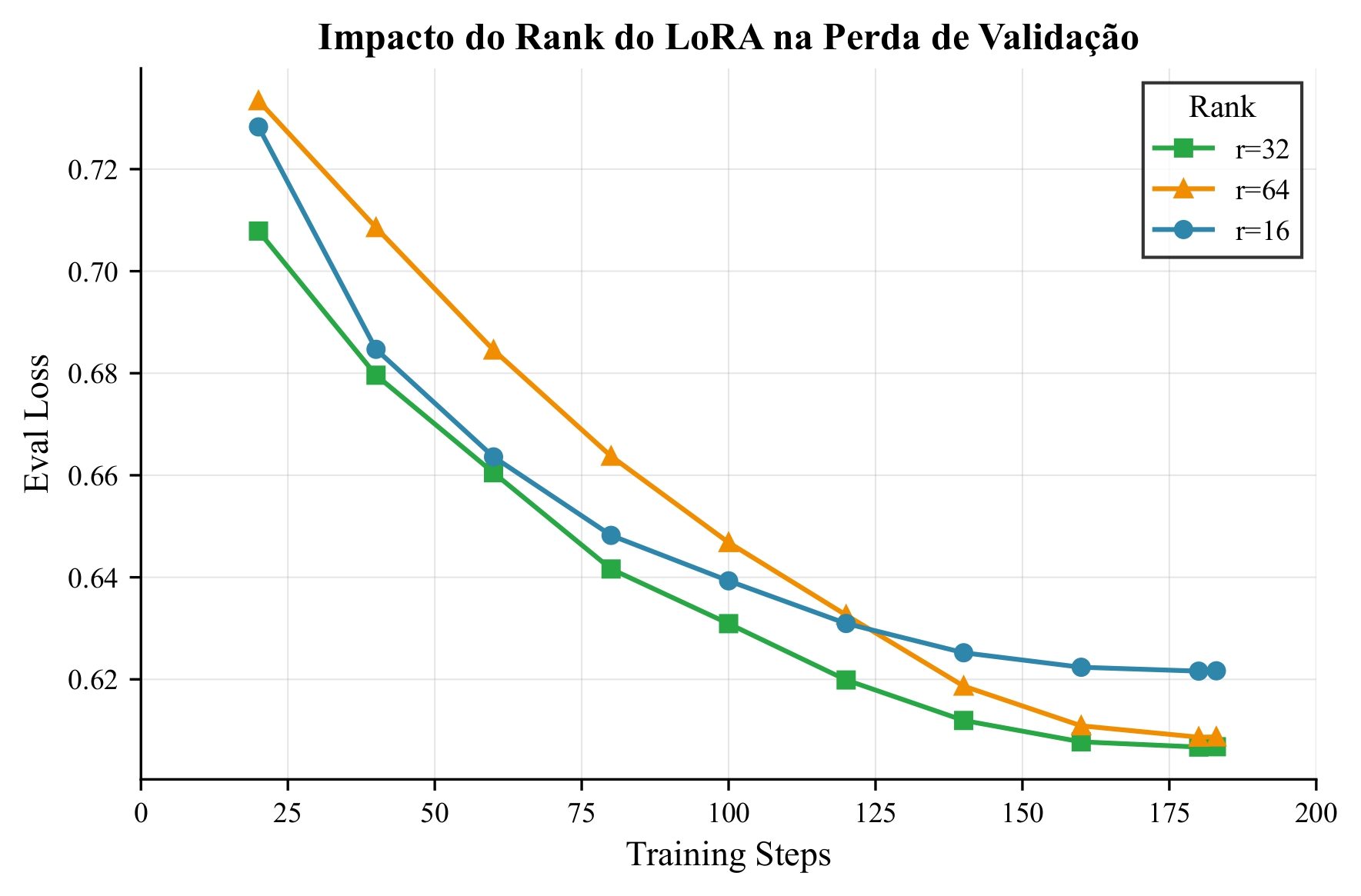
Impact of adapter rank on validation loss
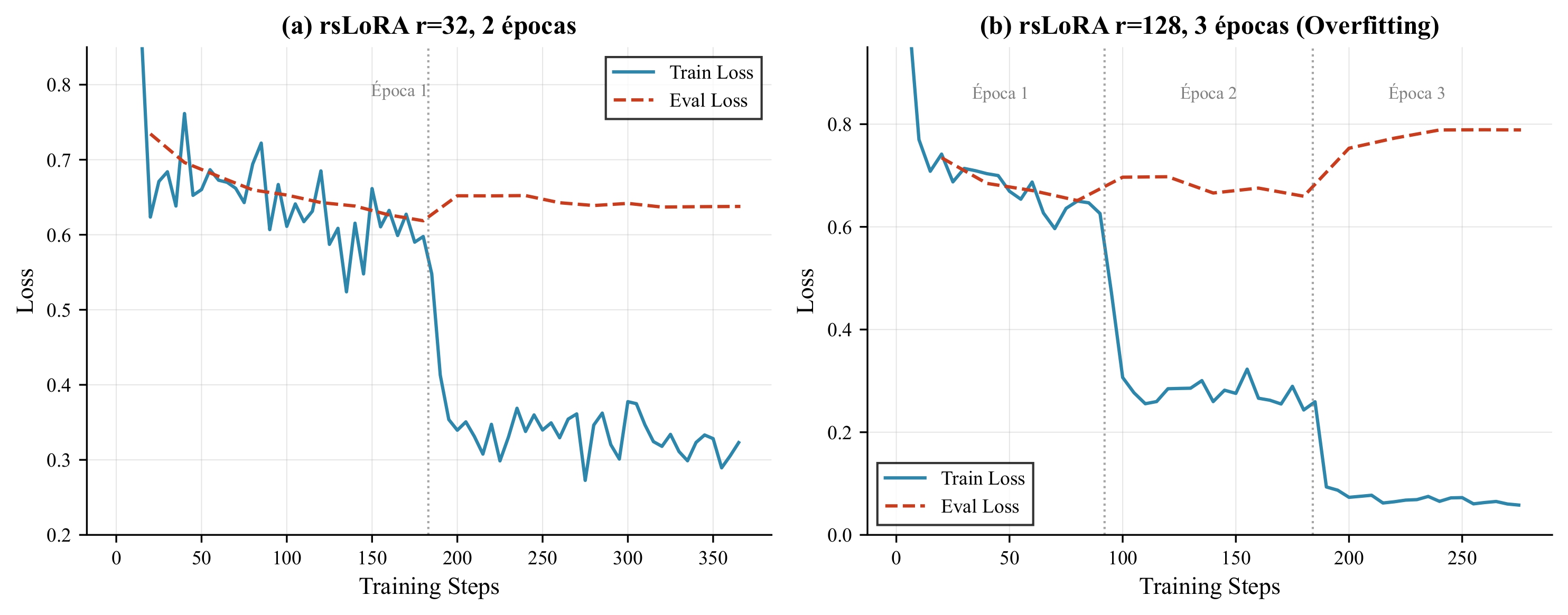
Overfitting analysis: (a) r32-2ep configuration, (b) r128-3ep configuration
Conclusions: rsLoRA with r=32 and 1-2 epochs maximizes generalization while avoiding memorization of the synthetic dataset.
Model Collection
This model is part of the Quantum Assistant collection. All models are merged versions ready for inference:
| Model | Configuration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Qwen3-VL-8B-rslora-r32-2 | rsLoRA r=32, 2 epochs | Best overall performance |
| Qwen3-VL-8B-rslora-r32 | rsLoRA r=32, 1 epoch | Best generalization |
| Qwen3-VL-8B-rslora-r64 | rsLoRA r=64, 1 epoch | Higher capacity |
| Qwen3-VL-8B-rslora-r128 | rsLoRA r=128, 1 epoch | Maximum capacity |
| Qwen3-VL-8B-lora | LoRA r=16, 1 epoch | Vanilla LoRA |
| Qwen3-VL-8B-dora | DoRA r=16, 1 epoch | Magnitude-direction decomposition |
| Qwen3-VL-8B-pissa | PiSSA r=16, 1 epoch | SVD initialization |
| Qwen3-VL-8B-olora | OLoRA r=16, 1 epoch | QR orthonormal initialization |
| Qwen3-VL-8B-rslora-frozen | rsLoRA r=16, frozen aligner | Ablation study |
| Qwen3-VL-8B-rslora | rsLoRA r=16, 1 epoch | Baseline rsLoRA |
Usage
With vLLM
python -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 8000 \
--model samuellimabraz/Qwen3-VL-8B-dora \
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.92 \
--max-model-len 12288 \
--max-num-seqs 16 \
--max-num-batched-tokens 49152 \
--enable-chunked-prefill \
--enable-prefix-caching
With Transformers
from transformers import Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration, AutoProcessor
from qwen_vl_utils import process_vision_info
model = Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"samuellimabraz/Qwen3-VL-8B-dora",
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("samuellimabraz/Qwen3-VL-8B-dora")
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a quantum computing expert assistant specializing in Qiskit."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Create a function that builds a 3-qubit GHZ state and returns the circuit."}
]
messages_with_image = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a quantum computing expert assistant specializing in Qiskit."},
{"role": "user", "content": [
{"type": "image", "image": "path/to/circuit.png"},
{"type": "text", "text": "Implement the quantum circuit shown in the image."}
]}
]
text = processor.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
image_inputs, video_inputs = process_vision_info(messages)
inputs = processor(
text=[text],
images=image_inputs,
videos=video_inputs,
padding=True,
return_tensors="pt"
).to(model.device)
generated_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=1024)
output = processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids[:, inputs.input_ids.shape[1]:],
skip_special_tokens=True
)[0]
print(output)
Training Details
Dataset
- Training Data: Quantum Assistant Dataset
- Train Samples: 5,837 (45.1% multimodal)
- Validation Samples: 1,239 (45.2% multimodal)
- Task Distribution: 30% function completion, 32% code generation, 38% QA
- Categories: 7 quantum computing domains
Training Configuration
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Base Model | Qwen/Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct |
| PEFT Method | DoRA (Weight-Decomposed LoRA) |
| Rank (r) | 16 |
| Alpha (α) | 32 |
| Dropout | 0.05 |
| Target Modules | all-linear |
| Learning Rate | 2e-4 |
| LR Scheduler | Cosine |
| Weight Decay | 0.01 |
| Warmup Steps | 10 |
| Epochs | 1 |
| Batch Size | 16 |
| Precision | bfloat16 |
| Framework | ms-swift |
Freezing Strategy
| Component | Status |
|---|---|
| Vision Encoder (ViT) | ❄️ Frozen |
| Vision-Language Aligner | 🔥 Trainable |
| Language Model (LLM) | 🔥 Trainable |
Training Infrastructure
- GPU: NVIDIA RTX PRO 6000 Blackwell Server Edition (96GB VRAM)
- Training Time: ~38.5 minutes (1 epoch)
- Tracking: Weights & Biases | TensorBoard
System Prompt
You are a quantum computing expert assistant specializing in Qiskit.
Provide accurate, clear, and well-structured responses about quantum computing concepts,
algorithms, and code implementation. Use Qiskit 2.0 best practices.
Intended Uses & Limitations
Intended Uses
- Educational assistance: Learning quantum computing concepts with Qiskit
- Code generation: Creating Qiskit circuits from descriptions or diagrams
- Documentation: Understanding quantum circuit visualizations
- Research prototyping: Rapid development of quantum algorithms
Limitations
- Domain specificity: Optimized for Qiskit 2.0; may generate deprecated APIs for older versions
- Dataset size: Trained on 5,837 samples; may underperform on rare edge cases
- Category imbalance: Better performance on
circuits_and_gatesthanprimitives_and_execution - Hardware specifics: Limited coverage of IBM Quantum hardware-specific optimizations
- Execution: Generated code requires verification before running on real quantum hardware
Bias and Risks
- Model may perpetuate patterns from training data
- Visual understanding limited to common diagram styles in Qiskit documentation
- May generate syntactically correct but logically incorrect quantum algorithms
- Should not be used for production quantum computing without human review
Citation
If you use this model in your research, please cite:
@misc{braz2025quantumassistant,
title={Quantum Assistant: Especializa{\c{c}}{\~a}o de Modelos Multimodais para Computa{\c{c}}{\~a}o Qu{\^a}ntica},
author={Braz, Samuel Lima and Leite, Jo{\~a}o Paulo Reus Rodrigues},
year={2025},
institution={Universidade Federal de Itajub{\'a} (UNIFEI)},
url={https://github.com/samuellimabraz/quantum-assistant}
}
Related Resources
- Dataset: samuellimabraz/quantum-assistant
- Model Collection: Quantum Assistant Models
- Demo: Quantum Assistant Space
- Code: GitHub Repository
Acknowledgments
- IBM Quantum and Qiskit team for open-source documentation
- Qwen Team for the base model
- UNIFEI (Universidade Federal de Itajubá) for academic support
- Advisor: Prof. João Paulo Reus Rodrigues Leite
License
This model is released under the Apache 2.0 License.
- Downloads last month
- 18
Model tree for samuellimabraz/Qwen3-VL-8B-dora
Base model
Qwen/Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct






